https://www.typescriptlang.org/docs/handbook/2/generics.html
Documentation - Generics
Types which take parameters
www.typescriptlang.org
Generics
function identity(arg: number): number {
return arg;
}
→ 숫자 타입의 파라마티 arg 변수를 입력받아, 숫자 타입의 arg 변수를 반환한다.
Generics가 왜 필요할까?
- CLI에서 echo command에서 자주 볼 수 있다.
- 입력된 값을 화면에 출력하는 데 사용된다.
- 사용자가 입력한 데이터가 예상한 형식인지 확인하는 타입 검증 목적으로 사용된다.
- 입력 값을 다른 함수에 전달하거나, 조건문에서 사용하여 프로그램의 흐름을 제어하는 연산의 기초로 활용한다.
- 사용자에게 입력한 값을 다시 보여줌으로써, 입력이 올바르게 처리되었음을 확인하기 위한 기초로 활용한다.
만약 다른 타입도 받을 수 있도록 하려면 어떻게 구성해야 할까?
function identity(arg: any): any {
return arg;
}
- any 타입을 이용할 수도 있다.
- 하지만 정확한 타입 검증의 목적을 달성하기 어려울 수 있다.
- number를 입력했는데 어떠한 요인에 의해서라도 변질된다면 string이 나와도 타입이 변한 것을 오류로 알 수 없다.
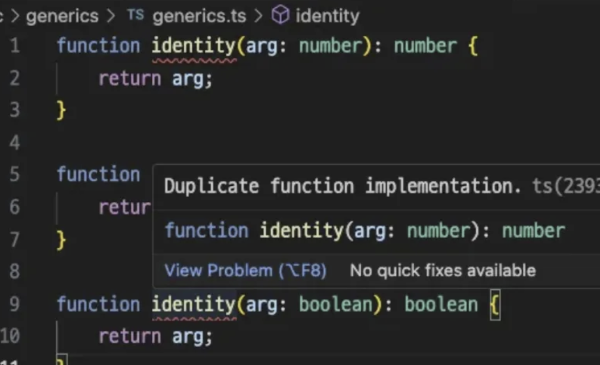
모든 타입마다 이것을 작성해야 하는가?
- 이것 또한 함수의 이름이 중복되어 허용되지 않는다.
function identityNum(arg: number): number {
return arg;
}
function identityStr(arg: string): string {
return arg;
}
function identityBool(arg: boolean): boolean {
return arg;
}
//...
function identityObj1(arg: obj1): obj1 {
return arg;
}
function identityObj2(arg: obj2): obj2 {
return arg;
}
interface obj1 {
//...
}
interface obj2 {
//...
}
//...
- 타입은 기본형 타입만 있지 않는다.
- 객체도 타입이 될 수 있고 따라서 수없이 많은 함수를 생성해야 하게 될 것이다.
➡️ 이런 비효율적인 상황을 대처하기 위한 것이 Generics이다.
- < > 안에 작성된 키워드가 해당 함수에 동일한 표현들을 동적으로 통일시킨다는 것을 나타낸다.
- 통일될 최초 타입은 키워드가 작성된 Parameter의 타입이 기준이 되며 해당 블록의 키워드가 포함된 타입들은 모두 이를 따르게 된다.
※ Type이란 키워드 대신 T라는 키워드로 대체하여 사용하는 경우가 많다.
// Use Generics
function identity<T>(arg: T): T {
return arg;
}- 참고 : Type 또는 T는 실제로 있는 자료형이 아니다.
자유롭게 지정할 수 있어 타입 별칭과 혼동될 수도 있지만 다른 기능이다.
관례적으로 T를 매개 변수가 2개 이상을 제너릭으로 표현해야 하는 경우엔 이후로는 U, V, W 등을 자주 사용해야 한다.
function identity<T, U>(arg1: T, arg2: U): [T, U] {
return [arg1, arg2];
}
const result = identity(20, "Hello"); // result는 [number, string] 타입
정확히 구분되는 테스트
function isNumber(value: any) {
return typeof value === 'number' && !isNaN(value);
}
function isString(value: any) {
return typeof value === 'string';
}
// isArray는 Array의 내장 함수 사용
// 간단 테스트
// given
const testValue1: number = 20;
const testValue2: string = "Hi";
const testValue3: number[] = [1, 20];
// when 1
const numberIdentity = identity(testValue1); // number 타입
// then 1
console.log(`Input type is : ${typeof testValue1}`);
console.log(`Output type is : ${typeof numberIdentity}`);
console.log(`Is number: ${isNumber(numberIdentity)}`); // true
// when 2
const stringIdentity = identity(testValue2); // string 타입
// then 2
console.log(`Input type is : ${typeof testValue2}`);
console.log(`Output type is : ${typeof stringIdentity}`);
console.log(`Is string: ${isString(stringIdentity)}`); // true
// when 3
const arrayIdentity = identity(testValue3); // number[] 타입
// then 3
console.log(`Input type is : ${typeof testValue3}`);
console.log(`Output type is : ${typeof arrayIdentity}`);
console.log(`Is array: ${Array.isArray(arrayIdentity)}`) // true- Generics를 사용한 identify() 함수가 예상대로 작동하는지 확인한다.
- 테스트 코드 작성의 Given - When - Then 패턴
- 준비 - 실행 - 검증의 단계로 테스트의 흐름이 명확하고, 각 단계에서 어떤 작업이 이루어지는지 쉽게 이해하기 위한 표현 기법
- Given : 테스트에 필요한 초기 데이터를 설정
- When : 테스트를 실행하는 부분으로, identity 함수를 호출
- Then : 각 입력 값에 대한 결과를 검증하고 출력
- 제너릭을 실제로 구현하고, 사용하기 어려울 수도 있지만 알고 있어야 하는 이유
- 사용하는 많은 함수, 메서드, 라이브러리 등은 이처럼 구현되어 있기 때문에 이는 다양한 데이터 타입을 쉽게 사용할 수 있도록 구현되어 있다.
- 필요에 따른 튜닝, 검토 등을 위해 내부 구조를 살펴보게 될 때 이해할 수 있어야 한다.
<Notion>
https://young-bug-a0f.notion.site/TypeScript-Generics-17f64001eaaf8029843ce1948ba725a0?pvs=74
TypeScript의 Generics | Notion
typescriptlang Documentation - Generics
young-bug-a0f.notion.site
728x90
SMALL
'프로그래밍 언어 > TypeScript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| TypeScript의 Modules (1) | 2025.01.22 |
|---|---|
| TypeScript의 Object, Class (2) | 2025.01.20 |
| TypeScript의 타입 - 2 (2) | 2025.01.20 |
| TypeScript의 타입 - 1 (1) | 2025.01.14 |
| TypeScript 기본 개념 (2) | 2025.01.10 |



